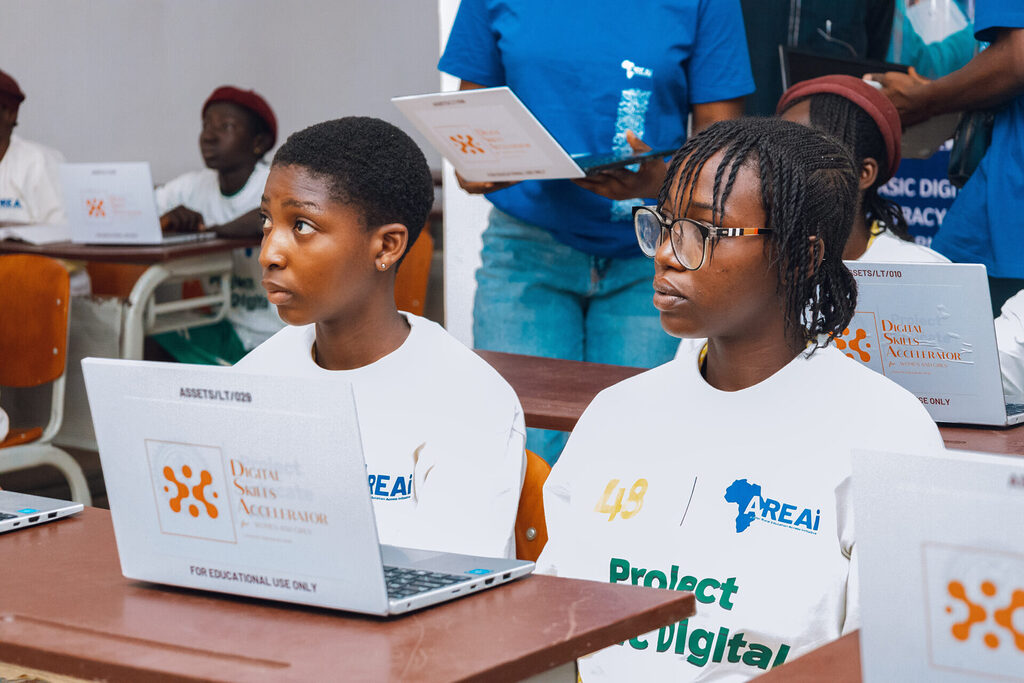
In an increasingly digital world, why should young African girls be left behind simply because they don’t have the tools or opportunities to learn and grow? For many girls, especially in underserved communities, access to technology is still out of reach. Limited resources, cultural expectations, gender-based discrimination, and outdated norms prevent them from exploring the tech and digital fields that could transform their lives.
Today, access to technology is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. Yet, the gender digital divide remains a powerful barrier. Without digital tools, reliable internet, and the skills to navigate a tech-driven society, these girls are left trapped in cycles of poverty and denied the chance to fulfil their potential. Therefore, taking critical steps through strategic partnerships and targeted funding is necessary. They can open doors for girls to gain the digital skills they need to succeed, empowering them to break barriers and create brighter futures.
The gender digital divide goes beyond access to technology; it also involves the ability of adolescent girls to learn relevant digital skills to use these technologies. According to a UNICEF analysis, approximately 90% of adolescent girls and young women in low-income countries remain offline. At the same time, their male peers are twice as likely to have access to the internet.
The consequences of this divide are far-reaching and severe. Without access to digital tools and skills, girls face educational setbacks, limited employment prospects, lower earning potential, and fewer opportunities to engage in global conversations about technology and innovation. This lack of digital literacy stifles their creativity and critical thinking and prevents them from actively contributing to economic and social development within their communities.
This divide must be bridged through equitable measures, as it is a critical step toward enabling girls to realize their full potential and ensuring that advancements in the digital era foster true inclusivity for all.
Addressing the gender digital divide requires more than individual efforts—it demands the collective strength of partnerships. Collaborative efforts between governments, NGOs, educational institutions, and the private sector are required. Strategic partnerships are essential in narrowing this gap, as they pool resources, expertise, and networks to implement programs that empower girls, particularly in underprivileged areas, with digital skills.
An example is the partnership between AREAi and 48percent.org for Project Basic Digital, which provided access to basic digital literacy skills to over 300 school girls in Nigeria. This collaboration speaks volumes about how strategic partnerships can equip and give adolescent school girls the training and mentorship they need to operate successfully in a continuously changing digital ecosystem.
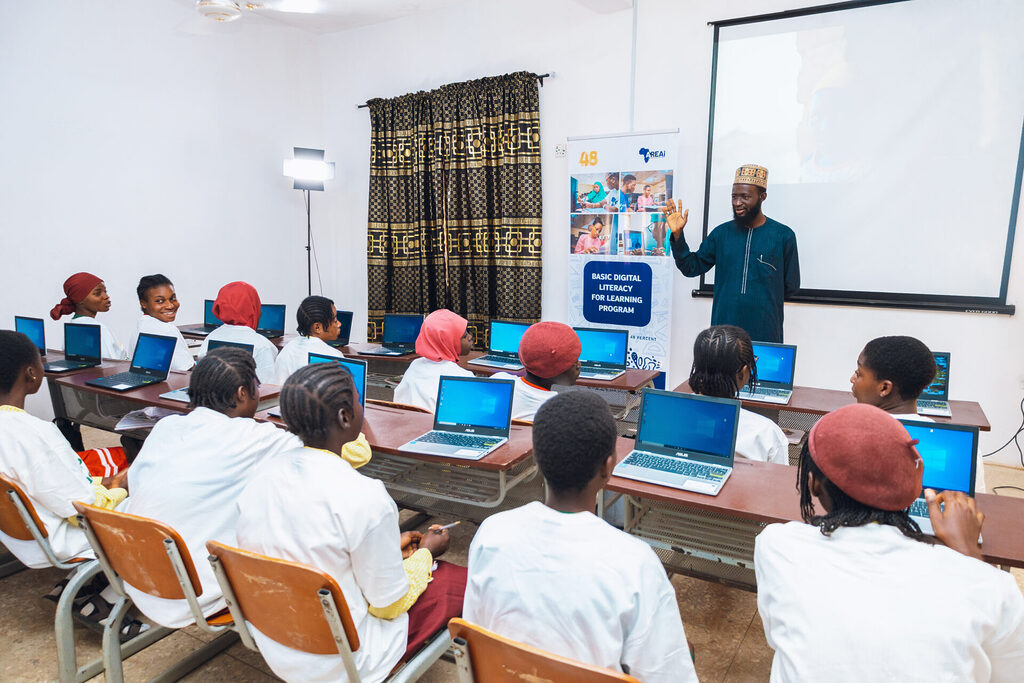

This way, girls from marginalized communities are acquiring formal education and technology-related skills, placing them at an advantageous position in the digital economy.
These partnerships, therefore, allow essential resources such as computers, internet connectivity, and learning platforms—primarily out of reach in marginalized communities—to be facilitated. Through strategic collaborations, the permutations and sharing of financial, technological, and human resources ensure that girls do, in reality, get digital training, infrastructure, and devices that they would otherwise not be in a position to afford, hence bridging the digital gap.
Strategic partnerships focus on capacity building in addition to increasing access to digital tools. Girls are empowered to participate in the digital economy through joint training programs, mentorship, and skill development in areas like basic digital literacy, coding, data science, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence. This not only helps them acquire valuable skills but also fosters confidence and independence as they engage with emerging technologies.
Finally, strategic partnerships play a crucial role in policy advocacy, driving changes that promote gender equality in the tech industry and challenge societal barriers limiting girls’ access to technology. Through collective efforts, these collaborations can influence policy changes that ensure digital rights for women and girls, create supportive ecosystems, and establish networks that encourage young girls to pursue careers and opportunities in technology. This helps create an inclusive digital environment where girls can thrive.
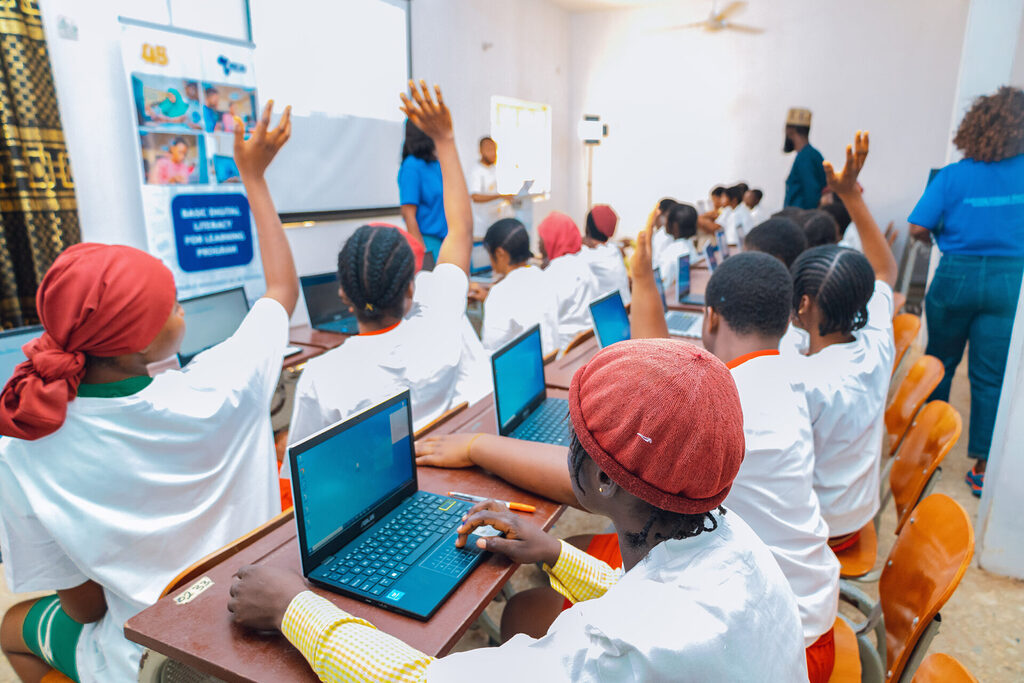

While partnerships are essential for collaboration, grants are the financial backbone supporting and scaling these initiatives. These grants enable NGOs to develop and implement programs to increase access to technology, digital literacy, and tech-related education for girls in underdeveloped communities.
Funding is required to purchase devices, training materials, and internet connectivity, ensuring that no girl is left behind due to financial constraints. Grants provide this vital funding source, making initiatives to bridge the digital divide possible.
Without grants, many of these initiatives would remain limited in scope. Funding makes it possible to cover the costs of materials and scale programs to reach more girls, especially in regions where access to tech resources is minimal. Through grants from national and international organizations, NGOs have been—and will continue to be—able to expand their projects to provide access to digital literacy and reach more girls in Africa.
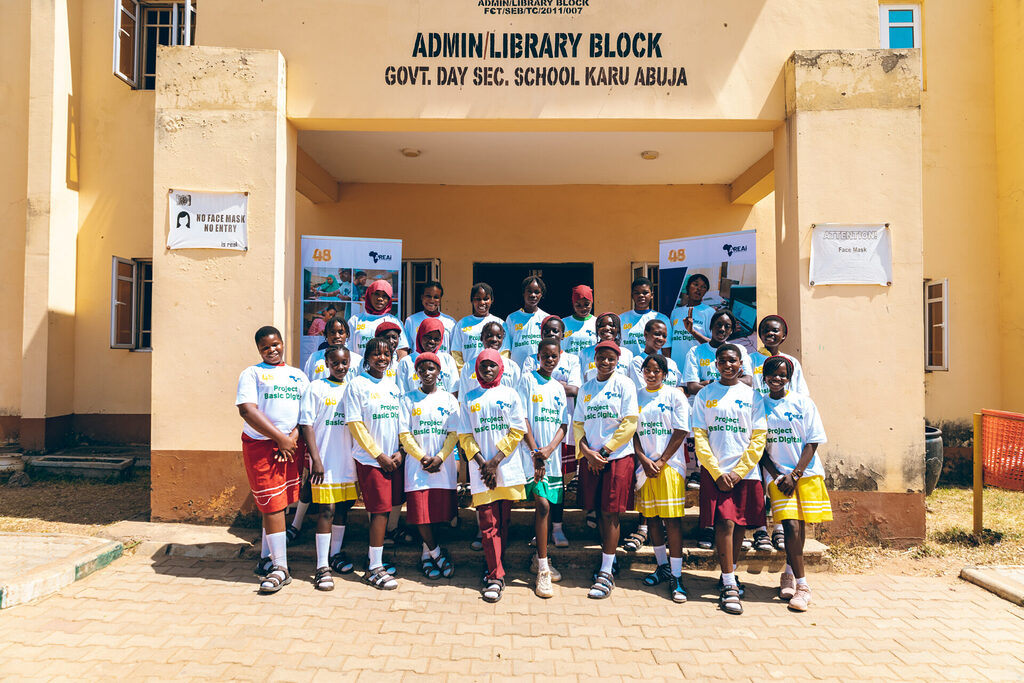

As we close this digital gap, international organizations and African corporations must invest in funding initiatives that provide digital skill training for girls, particularly in underserved communities. These organizations can help NGOs scale their programs, offer the technology they need, and ensure that no girl is left behind because of budgetary limitations by providing targeted grants and CSR funding. By giving this financing top priority, we can enable girls to acquire the skills necessary to succeed in the digital economy.
The fight to close the digital divide and empower girls with digital skills is far from over. Through strategic partnerships and targeted grants, we can help girls in marginalized communities become active agents of change rather than passive beneficiaries. Let us join hands to ensure that every girl in Africa has the tools needed to thrive in the digital age.
A girl who develops the competencies for using digital aids in her life is emerging as a creator, innovator, and leader rather than a passive receiver of change. Once given the support needed, they will bridge the gulf of the digital divide, find their places in the global digital economy, and bring transformation to their communities and the world in general.
UNICEF (2024). “90% of adolescent girls in low-income countries are offline. Available at: https://www.unicef.org/press-releases/90-cent-adolescent-girls-and-young-women-low-income-countries-are-offline-unicef
48percent. (2024). Basic Digital Literacy for Learning by AREAi. Available at: https://www.48percent.org/projects/basic-digital-literacy-for-learning-by-areai/
Written by:
Mary Okowori – Program and Impact Fellow (PIF)